Apache OpenDAL in Rust to Access Any Kind of Data Services
MarkdownView HTML version
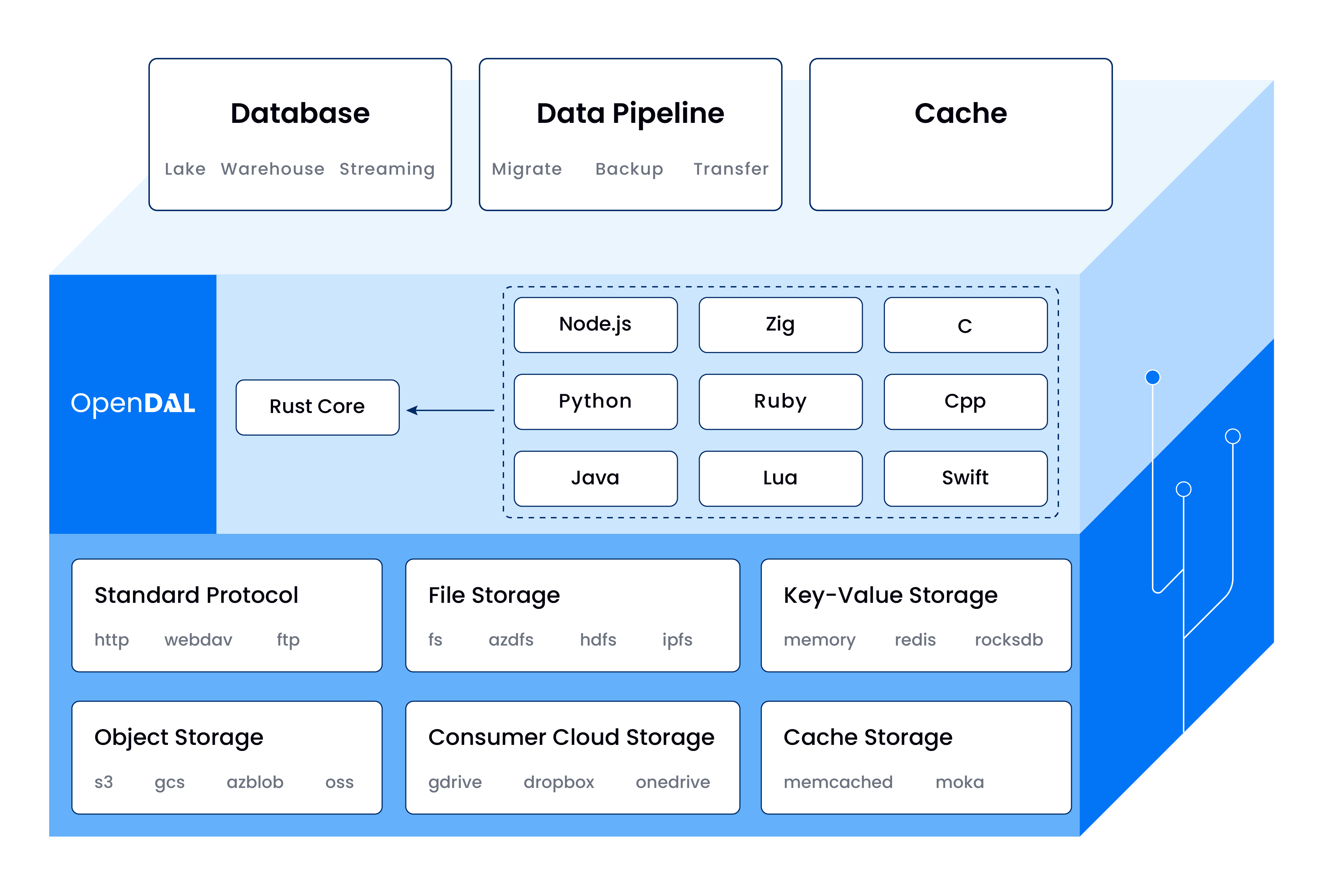
[OpenDAL](https://github.com/apache/incubator-opendal) is a data access layer that allows users to easily and efficiently retrieve data from various storage services in a unified way such as S3, FTP, FS, Google Drive, HDFS, etc. They has been rewritten in Rust for the Core and have a binding from many various language like Python, Node.js, C, etc.
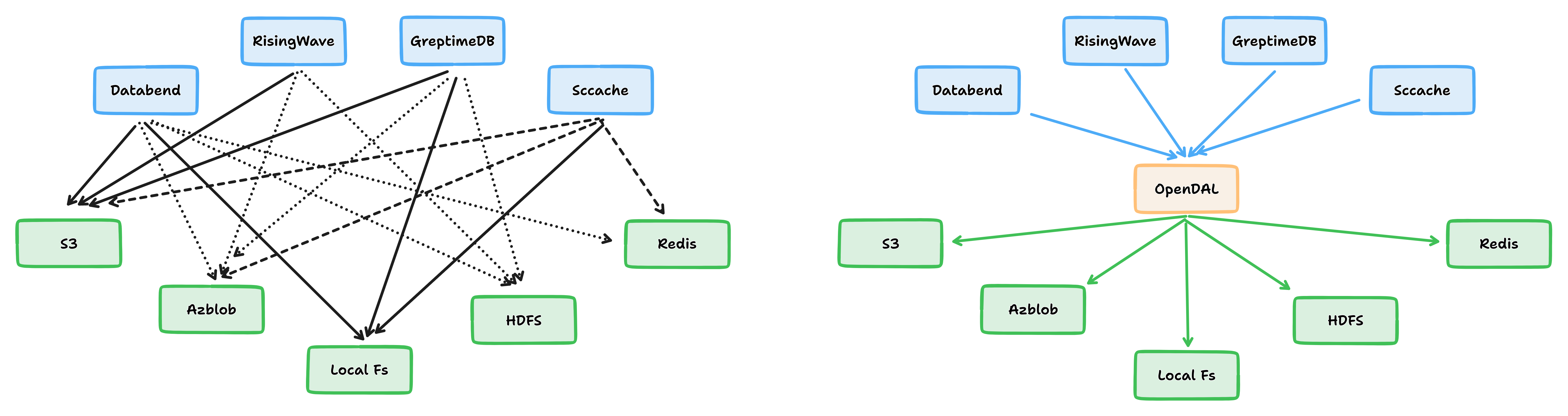
OpenDAL is designed for developers who need to build cloud-native, cross-cloud-first applications and services that **require configurable storage backends** to meet complex data access needs.
With OpenDAL, developers can use a unified interface to access multiple storage backends, including **cloud object storage, distributed file systems, and relational databases**. This allows developers to **easily switch** between different storage backends without having to worry about the underlying implementation details.
# Basic Usage
### 1. Via Builder
Typically, you will need to pick a **Builder** and configure it. After that, you initialize an Operator with the builder. This allows you to interact with the service, performing tasks such as **reading** or **writing** data.
For example, if we want to access to [S3 Service](https://opendal.apache.org/docs/services/s3)
```rust
use opendal::{services, Operator};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
// Pick a builder and configure it.
let mut builder = services::S3::default();
builder.bucket("my-bucket");
// Init an operator
let op = Operator::new(builder)?.finish();
// Read data
let bs = op.read("hello.txt").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
Look at the [**Configuration**](https://opendal.apache.org/docs/services/s3) section of each service so see the configuration keys to set for the service.
- `root`: Set the work dir for backend.
- `bucket`: Set the container name for backend.
- `endpoint`: Set the endpoint for backend.
- `region`: Set the region for backend.
- `access_key_id`: Set the access_key_id for backend.
- `secret_access_key`: Set the secret_access_key for backend.
- ...
### 2. Via Config
Another alternative is to create the `Operator` using a [`HashMap`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/std/collections/hash_map/struct.HashMap.html) as a construction method. You can refer to the [`Operator` documentation](https://docs.rs/opendal/latest/opendal/struct.Operator.html#method.via_map) for more information. This approach allows you to initialize operators based on dynamic configurations.
```rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
use opendal::{services, Operator, Scheme};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
// Config
let map = HashMap::from([
("bucket".to_string(), "my-bucket".to_string()),
]);
// Init an operator
let op = Operator::via_map(Scheme::S3, map)?;
// Read data
let bs = op.read("hello.txt").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
Seeing more at the Rust doc https://docs.rs/opendal
# Layers
OpenDAL also supporting [`layers`](https://docs.rs/opendal/latest/opendal/layers/index.html) like _logging, prometheus, tracing, timeout, retry, etc_.
```rust
use opendal::{services, Operator};
use opendal::layers::LoggingLayer;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
// Pick a builder and configure it.
let mut builder = services::S3::default();
builder.bucket("my-bucket");
// Init an operator
let op = Operator::new(builder)?
// Init with logging layer enabled.
.layer(LoggingLayer::default())
.finish();
// Read data
let bs = op.read("hello.txt").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
Look at some additional examples below
# FS - File System
[Document](https://opendal.apache.org/docs/services/fs) and [docs.rs](https://docs.rs/opendal/latest/opendal/services/struct.Fs.htmll)
```rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
use opendal::{Operator, Scheme};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.insert("root".to_string(), "/path/to/dir".to_string());
// Init an operator
let op: Operator = Operator::via_map(Scheme::Fs, map)?;
// Read data /path/to/dir/hello.txt
let bs = op.read("hello.txt").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
# HTTP
[Document](https://opendal.apache.org/docs/services/http) and [docs.rs](https://docs.rs/opendal/latest/opendal/services/struct.Http.html)
```rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
use opendal::{Operator, Scheme};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.insert("endpoint".to_string(), "127.0.0.1".to_string());
let op: Operator = Operator::via_map(Scheme::Http, map)?;
// Read data http://127.0.0.1/hello.txt
let bs = op.read("hello.txt").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
# Example: function support to read CSV file from local/s3/http
```rust
use anyhow::{Context, Result};
use opendal::{Operator, Scheme};
use url::Url;
async fn read_file(path: &str) -> Result<()> {
// Extract the file name from the path
let file_name = path.split('/').last().unwrap_or_default();
// Local file, start with '/'
let (scheme, args) = if path.starts_with('/') {
let root = path.trim_end_matches(file_name).to_string();
(Scheme::Fs, {
let mut args = std::collections::HashMap::new();
args.insert("root".to_string(), root);
args
})
} else {
// Parse the URL to determine the scheme
let url = Url::parse(path)?;
// Determine the scheme and create OperatorArgs accordingly
match url.scheme() {
"file" => (Scheme::Fs, {
let mut args = std::collections::HashMap::new();
args.insert("root".to_string(), url.path().to_string());
args
}),
"http" | "https" => (Scheme::Http, {
let mut args = std::collections::HashMap::new();
args.insert(
"endpoint".to_string(),
url.host_str().unwrap_or_default().to_string(),
);
args
}),
"s3" => (Scheme::S3, {
let mut args = std::collections::HashMap::new();
args.insert(
"bucket".to_string(),
url.host_str().unwrap_or_default().to_string(),
);
if !url.path().is_empty() {
args.insert("key".to_string(), url.path()[1..].to_string());
}
args
}),
_ => {
return Err(anyhow::anyhow!("Unsupported scheme"));
}
}
};
// Create an Operator instance and read the CSV file
let op: Operator = Operator::via_map(scheme, args)?;
// Read the CSV file
let content = op
.read(file_name)
.await
.with_context(|| format!("Failed to read from: {}", path))?;
// For now, just print the data
println!("{:?}", content);
Ok(())
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
read_file("/tmp/aaa").await?;
read_file("file:///tmp/aaa").await?;
read_file("https://example.com/path/to/http/file2.csv").await?;
read_file("s3://bucketname/path/to/s3/file3.csv").await?;
Ok(())
}
```
Get and run the example code in my repository on GitHub [`duyet/opendal-examples`](https://github.com/duyet/opendal-examples/tree/master)
# References
- [Apache OpenDAL GitHub](https://github.com/apache/incubator-opendal)
- [Apache OpenDAL Documentation](https://opendal.apache.org/docs)
- [docs.rs/opendal](https://docs.rs/opendal)
- ["OpenDAL Examples Repository on GitHub"](https://github.com/duyet/opendal-examples) by duyet.